Abstract
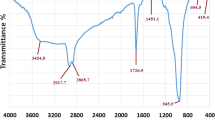
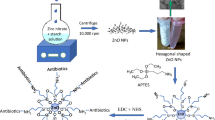
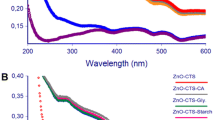
Biofilm formation hinders the activity of antimicrobial drugs at the site of infections and any agent that can act on both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by inhibiting the bacterial growth and rupturing the biofilm is needed to manage infection. In the present study, we have synthesized zirconia nanoparticles (ZrO2 NPs) and copper doped zirconia nanoparticles (Cu-ZrO2 NPs) and characterized them using dynamic light scattering, X-ray diffractometry, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The size of the Cu-ZrO2 NPs drastically reduced compared to ZrO2 NPs, and the antimicrobial activity was studied against Gram-positive bacteria (Lactobacillus sp.) and Gram-negative bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), respectively. The synthesized Cu-ZrO2 NPs showed superior inhibitory action against Lactobacillus sp. compared to ZrO2 NPs, due to the negatively charged cell wall of Lactobacillus sp., which could attract readily the positively charged Cu-ZrO2 NPs, thereby inhibiting its activity. The biocompatibility was tested using XTT assay in FL cells, and the results demonstrated that Cu-ZrO2 NPs were nontoxic to mammalian cells. Hence, it could be proposed that the synthesized Cu-ZrO2 NPs possess possible biomedical applications and can be used as antibacterial agents without causing toxicity in mammalian cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puzyn, T., Rasulev, B., Gajewicz, A., Hu, X., Dasari, T. P., Michalkova, A., Hwang, H. M., Toropov, A., Leszczynska, D., & Leszczynski, J. (2011). Using nano-QSAR to predict the cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol., 6, 175–178.
Sung, L-P, Scierka, S., Baghai-Anaraki, M. and Ho, D.L.: Characterization of metal-oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and dispersion in polymeric coatings, 2003 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., 7401, 15.4.1-15.4.6 (2003).
Girigoswami, K., Viswanathan, M., Murugesan, R., & Girigoswami, A. (2015). Studies on polymer-coated zinc oxide nanoparticles: UV-blocking efficacy and in vivo toxicity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 56, 501–510.
Dreher, K. L. (2004). Health and environmental impact of nanotechnology: Toxicological assessment of manufactured nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci., 77, 3–5.
Aricò, A., Bruce, P., Scrosati, B., Tarascon, J.-M., & van Schalkwijk, W. (2005). Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nature Mater., 4, 366–377.
Song, Z., Cai, T., Chang, Z., Liu, G., Rodriguez, J. A., & Hrbek, J. (2003). Molecular level study of the formation and the spread of MoO3 on Au(111) by scanning tunneling microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 8059–8066.
Lim, H., Ahmad, A., & Hamzah, H. (2013). Synthesis of zirconium oxide nanoparticle by sol-gel technique. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1571, 812. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4858755
Behbahani, A., Rowshanzamir, S., & Esmaeilifar, A. (2012). Hydrothermal synthesis of zirconia nanoparticles from commercial zirconia. Procedia Engineering, 42, 908–917.
Geuzens, E., Vanhoyland, G., D’Haen, J., Van Bael, M. K., Van den Rul, H., Mullens, J., & Van Poucke, L. C. (2004). Synthesis of tetragonal zirconia nanoparticles via an aqueous solution-gel method. Key Engineering Materials, 264–268, 343–346.
Maridurai, T., Balaji, D., & Sagadevan, S. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of yttrium stabilized zirconia nanoparticles. Materials Res., 19, 812–816.
Thakare, V., Joshi, P., Godse, R., Bhatkar, V., Wadegaokar, P., & Omanwar, S. K. (2016). Evaluation of biological activities of nanocrystalline tetragonal zirconia synthesized via sol-gel method. Int. J. Pharmacy Pharmaceut. Sci., 8, 125–131.
Gupta, P. K., Pachauri, N., Khan, Z. H., & Solanki, P. R. (2017). One pot synthesized zirconia nanoparticles embedded in amino functionalized amorphous carbon for electrochemical immunosensor. J. Electroanal. Chem., 807, 59–69.
Lakusta, M., Danilenko, I., Konstantinova, T., & Volkova, G. (2016). Influence of obtaining conditions on kinetics of the initial sintering stage of zirconia nanopowders. Nanoscale Res. Lett., 11, 238. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1452-3
Chen, Y. W., Moussi, J., Drury, J. L., & Wataha, J. C. (2016). Zirconia in biomedical applications. Expert Rev. Med. Devices, 13(10), 945–963.
Asadi, S., Abdizadeh, H., & Vahidshad, Y. (2012). Effect of crystalline size on the structure of copper doped zirconia nanopaticles synthesized via sol-gel. J. Nanostructures, 2(2), 205–212.
Girigoswami, A., Ramalakshmi, M., Akhtar, N., & Metkar., S. K. and Girigoswami, K. (2019). ZnO Nanoflower petals mediated amyloid degradation - An in vitro electrokinetic potential approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 101, 169–178.
Mftah, A., Alhassan, F. H., Al-Qubaisi, M. S., El Zowalaty, M. E., Webster, T. J., Sh-Eldin, M., Rasedee, A., Taufiq-Yap, Y. H., & Rashid, S. S. (2015). Physicochemical properties, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial activity of sulphated zirconia nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomedicine., 10, 765–774.
O'Toole, G. A. (2011). Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J. Vis. Exp., 47, 2437.
Liu, K., Liu, P. C., Liu, R., & Wu, X. (2015). Dual AO/EB staining to detect apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells compared with flow cytometry. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res., 21, 15.
Metkar, S. K., Girigoswami, A., Murugesan, R., & Girigoswami, K. (2017). In vitro and in vivo insulin amyloid degradation mediated by Serratiopeptidase. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 70, 728–735.
Bharadwaj, K. K., Rabha, B., Pati, S., Choudhury, B. K., Sarkar, T., Gogoi, S. K., Kakati, N., Baishya, D., Kari, Z. A., & Edinur, H. A. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Diospyros malabarica fruit extract and assessments of their antimicrobial, anticancer and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Nanomaterials, 11(8), 1999.
Nag, M., Lahiri, D., Sarkar, T., Ghosh, S., Dey, A., Edinur, H. A., Pati, S. and Ray, R. R.: Microbial fabrication of nanomaterial and its role in disintegration of exopolymeric matrices of biofilm. Frontiers in chemistry, 9 (2021).
Rabha, B., Bharadwaj, K. K., Baishya, D., Sarkar, T., Edinur, H. A., & Pati, S. (2021). Synthesis and characterization of diosgenin encapsulated poly-ε-caprolactone-pluronic nanoparticles and its effect on brain cancer cells. Polymers, 13(8), 1322.
Aas, J. A., Griffen, A. L., Dardis, S. R., Lee, A. M., Olsen, I., Dewhirst, F. E., Leys, E. J., & Paster, B. J. (2008). Bacteria of dental caries in primary and permanent teeth in children and young adults. J Clin Microbiol., 46(4), 1407–1417.
Øilo, M., & Bakken, V. (2015). Biofilm and dental biomaterials. Materials, 8(6), 2887–2900.
Nistor, L., Grădinaru, M., Rîcă, R., Mărășescu, P., Stan, M., Manolea, H., Ionescu, A., & Moraru, I. (2019). Zirconia use in dentistry - Manufacturing and properties. Current health sciences journal, 45(1), 28–35.
Volpato, C.Â.M., ́Altoé Garbelotto, L.G.D., Fredel, M.C. and Bondioli, F. Application of zirconia in dentistry: biological, mechanical and optical considerations, In “Advances in ceramics-electric and magnetic ceramics, bioceramics, ceramics and environment”, Intech Open, 2011.
Lboutounne, H. (2017). Dental Medicine Nanosystems: Nanoparticles and their use in dentistry and oral health care. Int J Dent & Oral Heal., 3(10), 145–157.
Afra, S., & Modaresi, F. (2017). The use of synergistically antiplaque nanoparticles in treating dental caries. J Dent Health Oral Disord Ther., 6(5), 144–147.
Pitts, N., Zero, D., Marsh, P., et al. (2017). Dental caries. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 3, 17030.
Kaur, N., Sahni, P., Singhvi, A., Hans, M. K., & Ahluwalia, A. S. (2015). Screening the drug resistance property among aerobic pathogenic microorganisms of dental caries in north-western Indian population: A preliminary study. J Clin Diagn Res., 9(7), ZC05-ZC8.
Askar, H., Krois, J., Göstemeyer, G., et al. (2020). Secondary caries: What is it, and how it can be controlled, detected, and managed? Clin. Oral Invest., 24, 1869–1876.
Chikere, C. O., Faisal, N. H., Kong-Thoo-Lin, P. and Fernandez, C.: Interaction between amorphous zirconia nanoparticles and graphite: Electrochemical applications for gallic acid sensing using carbon paste electrodes in wine, Nanomaterials (Basel) 10, 537 (2020).
Singh, A. K. and Nakate, U. T.: Microwave synthesis, characterization, and photoluminescence properties of nanocrystalline zirconia, Scientific World J., 2014, 349457 (2014).
Cabal, B., Cafini, F., Esteban-Tejeda, L., Alou, L., Bartolomé, J. F., Sevillano, D., López-Piriz, R., Torrecillas, R., & Moya, J. S. (2012). Inhibitory effect on in vitro Streptococcus oralis biofilm of a soda-lime glass containing silver nanoparticles coating on titanium alloy. PLoS One, 7, e42393.
Afra, S. M., & Modaresi, F. (2017). The use of synergistically antiplaque nanoparticles in treating dental caries. J. Dent. Oral Disord. Ther., 6, 00214.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Chettinad Academy of Research and Education for providing the infrastructural support. The authors acknowledge funding from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), INDIA, Scheme No. 01(2868)/17/EMR-II.
Data Availability
All the authors declare that all data and materials support their published claims and comply with field standards.
Code Availability
Not applicable
Funding
The study was funded by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India, Scheme No. 01(2868)/17/EMR-II.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nishakavya S, Divya A, Deepa R, Ajith S, and Gopikrishna A have executed the experiments. Agnishwar Girigoswami and Koyeli Girigoswami have given the concept and prepared the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
• The manuscript has not been submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration.
• The submitted work is original and should not have been published elsewhere in any form or language (partially or in full).
• A single study is not split up into several parts to increase the quantity of submissions and submitted to various journals or to one journal over time (i.e., “salami-slicing/publishing”).
• Results are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation (including image-based manipulation). The authors have adhered to discipline-specific rules for acquiring, selecting, and processing data.
• No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the author’s own (“plagiarism”). Proper acknowledgements to other works have been given.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 186 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishakavya, S., Girigoswami, A., Gopikrishna, A. et al. Size Attenuated Copper Doped Zirconia Nanoparticles Enhances In Vitro Antimicrobial Properties. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 3435–3452 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03875-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03875-y